Building a successful customer experience (CX) program isn’t easy for any organization, however B2B (business-to-business) firms have a variety of extra complexities to contend with, including:
- Multiple client roles. B2B “customers” are not a single person, but typically involve multiple stakeholders who are in different roles within the client’s organization, like decision makers, influencers, and users. These different roles each have varying levels of involvement in the customer relationship over time, and creating a targeting, sampling, and data collection approach that captures insights from the right people at the right time and in the right way can be difficult.
- Multi-faceted relationship model. Multiple functions in B2B organizations have the potential to impact customers’ experiences and require different insights to support their work. For example, customer support needs insights to fuel effective recovery efforts, while product teams need insights to ingrain customer-centric thinking in design processes. However, B2B’s siloed nature impacts the firm’s ability to have a shared approach across a customer’s entire experience.
- Respondent sample limitations. B2B organizations inherently have fewer customers and hard-to-reach key decision makers. In order to get accurate information from these small populations, they need to carefully curate and target their feedback sampling strategy through strong partnerships with account managers and/or sales teams – or else get creative with advisory boards, user groups, etc.
To understand how B2B organizations are performing, we collect data from CX practitioners who specifically work at B2B companies and can provide insight into the particular status of B2B CX programs. In 2024, respondents shared a variety of information around their CX management programs and completed both our CX Competency and Maturity Assessment and our new (as of 2023) XM-Centric Culture Assessment.
In this blog post, we’re diving into the state of B2B CX management in 2024 and how it compares to some of the results we gathered from a similar study conducted in 2022.
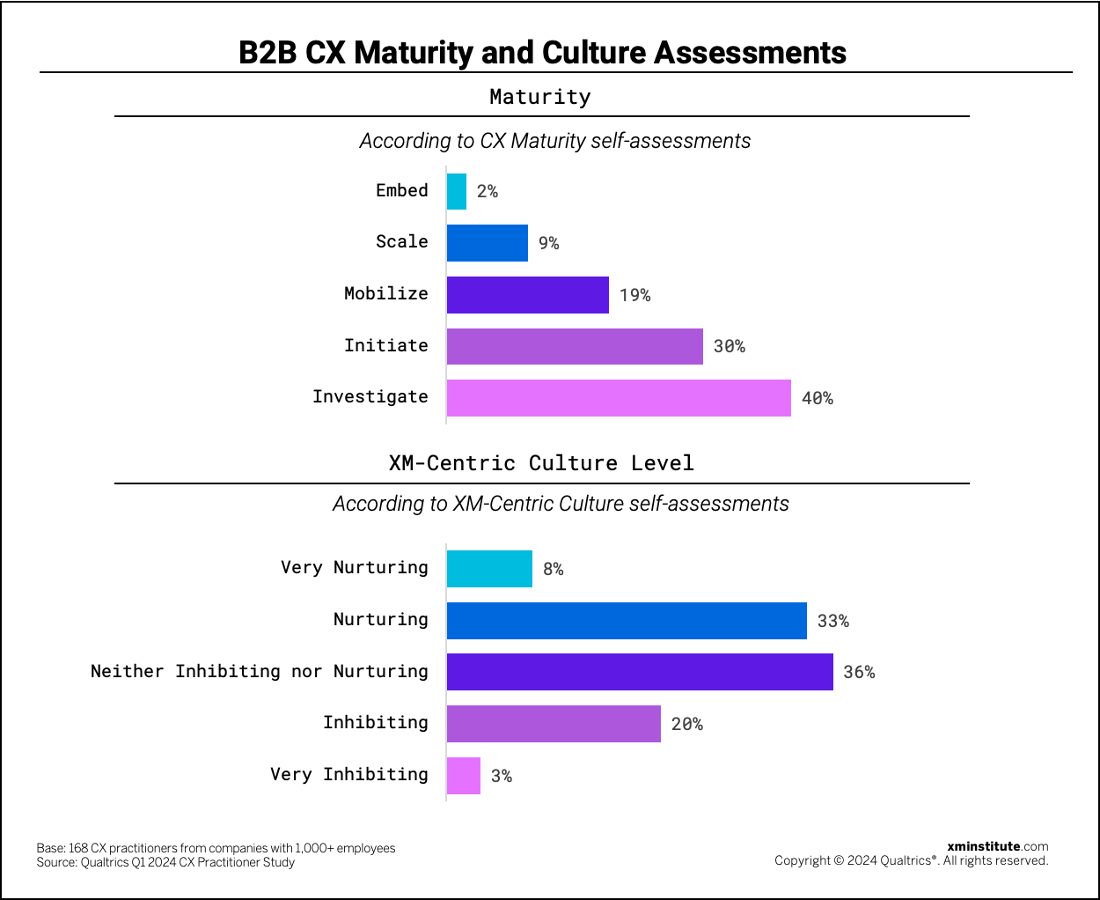
When we review B2B CX management at a high level, we see that:
- B2B CX maturity still has room to grow… While 11% of B2B CX practitioners evaluated their organizations to be the top two stages of maturity – Embed (2%) and Scale (9%) – we found that the majority of B2B organizations (70%) fall into the first two stages of maturity, with 40% in the Investigate stage and 42% in the Initiate stage.
- … but continues to improve. Compared to the results of our 2022 B2B CX maturity assessment, we see a moderate increase in B2B maturity levels. In 2022, just 23% of B2B organizations were in the Mobilize, Scale, or Embed stages of CX maturity, while 30% have reached one of these three stages in 2024.
- B2B organizational cultures are ready for XM. Forty-one percent of B2B organizations have nurturing or very nurturing XM-Centric cultures, according to our new XM-Centric Culture level assessment. Only 23% of CX professionals find their organizational cultures to be inhibiting or very inhibiting to XM practices.
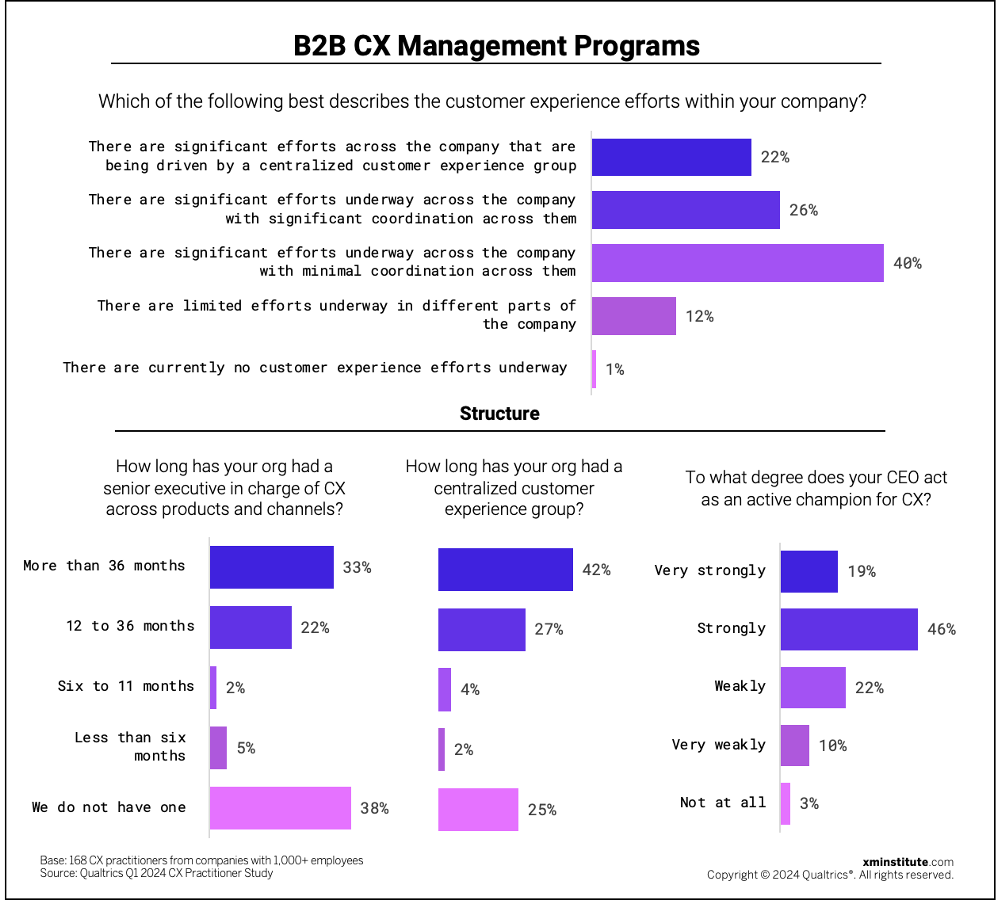
When we looked a little deeper into the composition of the CX programs at these B2B firms, we found that:
- Significant CX efforts are underway. Eighty-eight percent of B2B respondents say they have significant CX efforts underway across the company – about the same as in 2022 (90%). While 40% say these significant efforts are conducted with minimal coordination, 48% say their efforts enjoy either significant coordination (26%) or are driven by a centralized CX group (22%).
- Three-quarters of B2B firms have a centralized CX group. Nearly 70% of B2B organizations have had a centralized CX group in place for a year or more,while 25% of B2B respondents say they don’t have a central team at all. 41% enjoy CX team sizes of more than 10 full-time employees, which is 10 points up from 31% just two years ago. However, of the organizations that do benefit from a centralized CX group, over one-third (37%) have five employees or fewer.
- Under two-thirds of B2B firms have a senior CX leader. Sixty-two percent of B2B CX practitioners have a senior executive in charge of CX across products and channels, and the majority of these roles have existed for 36 months or longer. Sixty-five percent describe their CEO (or equivalent organizational leader) as a strong or very strong active champion for CX efforts.
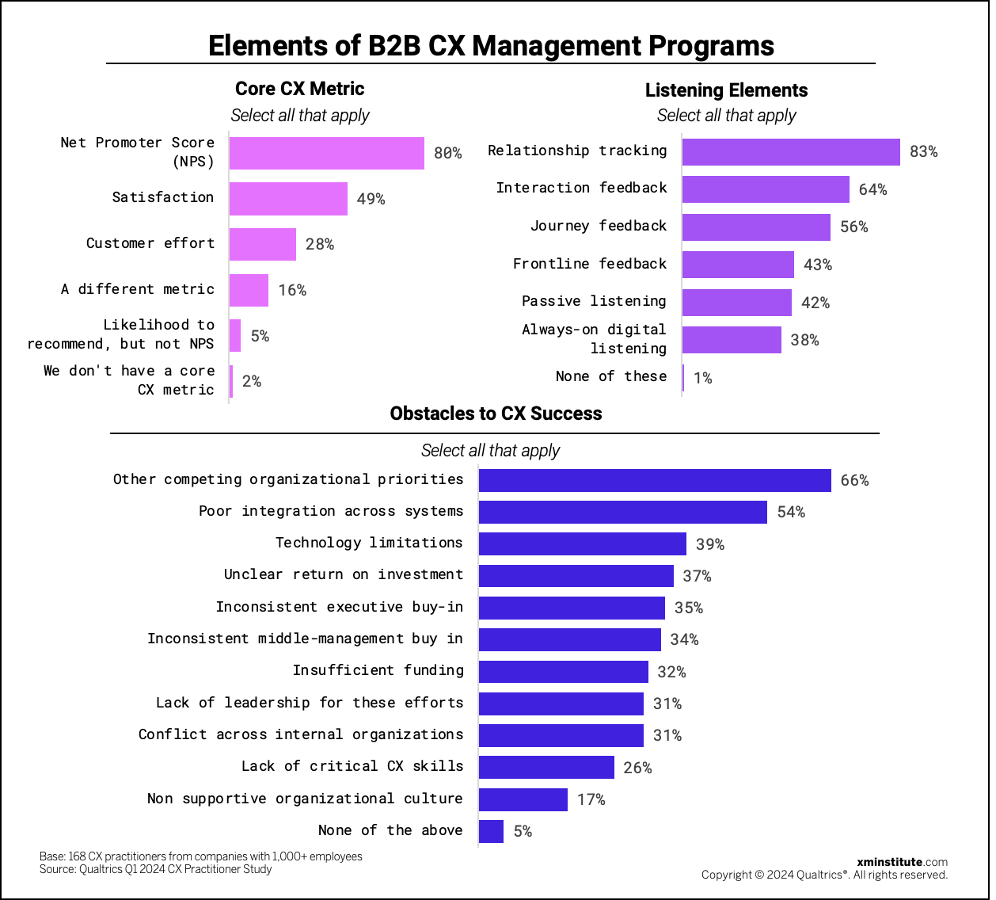
We also asked B2B respondents about their primary customer experience metric(s), which elements compose their CX listening portfolio, and whether they’ve encountered some of the common pitfalls that can curb CX program progression. Their answers tell us that:
- Four in five B2B firms use NPS. Eighty percent of B2B respondents say their organization uses NPS (Net Promoter Score®) as a core CX metric, making it the most commonly used measurement. Satisfaction ranks second, with 49% of B2B firms using it as a core metric, while CES (customer effort) falls in third at 28%. Respondents are more likely to report using each of these three measurements – as well as a different metric – than in 2022, indicating that B2B practitioners are finding valuable nuance in what the different metrics have to offer.
- Most B2B firms track relationship health. Over 80% of B2B CX practitioners report that their organization conducts relationship tracking as part of their CX listening program. Sixty-four percent collect interaction feedback, and 56% collect journey feedback. Fewer than half track frontline feedback (43%), conduct passive listening (42%), or include always-on digital listening (38%) elements in their CX program.
- Prioritizing CX remains a challenge for B2B. Sixty-six percent of B2B respondents cited other competing organizational priorities as a top obstacle to CX success, which was also the most frequently encountered challenge in 2022. Similar to two years ago, B2B CX practitioners still consider poor integration across systems (54%) as the second-largest obstacle to overcome. Respondents in 2024 least frequently cited non supportive organizational culture (17%), indicating that their organizational cultures are largely ready to nurture XM, as we also learned from the XM-centric culture assessment.
For additional guidance on advancing your CX program, check out all our B2B-related content in our XM Library.
The bottom line: B2B CX programs are on the up-and-up, but still encounter challenges.
Talia Quaadgras is a Research Program Manager for Qualtrics XM Institute
Isabelle Zdatny, XMP, CCXP, is Head of Thought Leadership for Qualtrics XM Institute





