Use this Launchpad as a starting place to understand what Digital Experience Management (Digital XM) is and how to establish a strong Digital XM program. Then explore the key resources included at the bottom of the page to expand your knowledge of this essential XM topic.
The Fundamentals
Digital Experience Management (Digital XM) refers to
The discipline of combining operational data (O-Data) and experience data (X-Data) to design and improve people’s experiences through an organization’s digital channels, including the web, mobile apps, social channels, or connected devices.
By their very nature, digital experiences create XM opportunities that other channels don’t. They automatically generate significant amounts of operational data. They offer a smoother, less disruptive medium for collecting feedback. They provide a controlled environment that makes it easier to iterate on and improve experiences at scale. Not to mention, digital is now a – if not the – primary interaction channel for most companies.
To capitalize on all these opportunities, organizations need to establish a strong Digital XM program – one that is capable of continuously collecting and analyzing feedback and signals from visitors and then using those insights to, not only design and improve people’s experiences through digital channels, but with the organization at large.
Six Digital XM Competencies
To develop their Digital XM capabilities, organizations should adopt the XM Operating Framework. The XM Operating Framework is a blueprint that lays out how organizations can master Experience Management by leveraging their technology and culture to build six XM Competencies:
Lead
Building an effective Digital XM program will require an organization to articulate a clear digital strategy and then coordinate the execution of that strategy across a number of different people and projects over multiple years. This Competency is about architecting, aligning, and sustaining successful Digital XM efforts.
Realize
For Digital XM efforts to have a lasting positive impact, they need to generate strategic and financial value for the organization. This Competency is about identifying and tracking the right metrics to ensure Digital XM efforts achieve well-defined business objectives.
Activate
People tend to gravitate towards the status quo, so a successful Digital XM program must overcome people’s inertia and their natural resistance to change. This Competency is about making sure that the organization has the appropriate skills, support, and motivation to achieve desired Digital XM results.
Enlighten
To improve the experiences it delivers through its digital channels, an organization must be capable of collecting and processing a constant flow of experience and operational data through these channels and then transforming it into useful information. This Competency is about capturing, analyzing, and distributing actionable insights.
Respond
Gathering and disseminating insights is all well and good, but ultimately, value is only generated when an organization acts on what it learns. This Competency is about building organizational mechanisms to continuously take action based on Digital XM insights.
Disrupt
While finding and fixing problems is necessary, just responding to explicit issues is not sufficient to capture people’s hearts and minds. This Competency is about identifying and creating digital experiences that differentiate the organization from its competitors.
Digital XM Application Areas
Once an organization begins building its Digital XM Competencies, how should it apply these newfound capabilities to improve experiences across the business? Here are some common application areas:
User Experience Improvement
Organizations should use the insights they capture through their Digital XM program to create intuitive, enjoyable digital interfaces that are easy for visitors to understand and navigate.
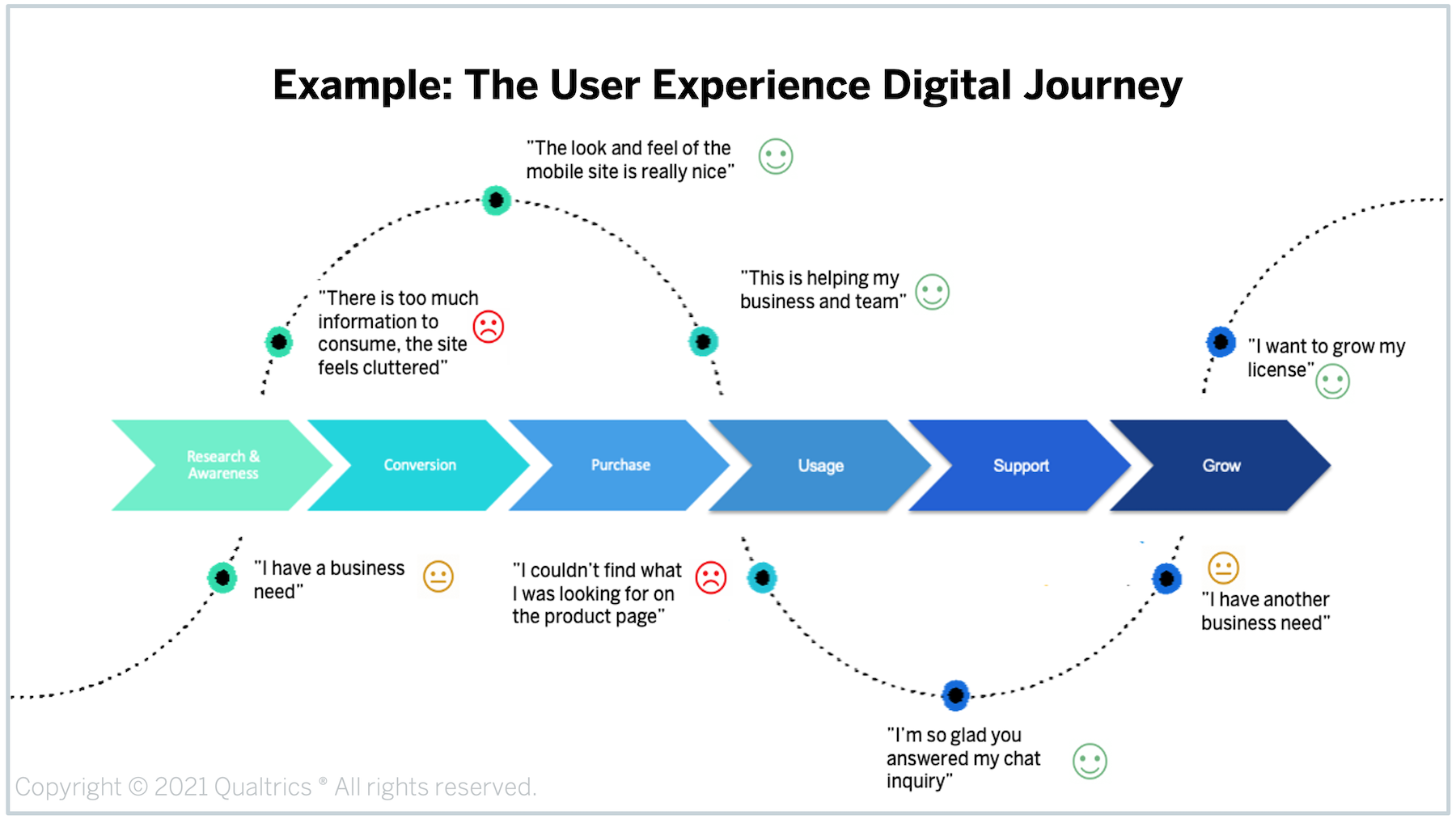
Journey Optimization
Digital XM programs should help organizations recognize the high-level goals their visitors are trying to achieve – like gathering information, managing their account, getting support, or making a purchase – and then use those insights to prioritize and improve pain points at key points along their journey.
Content Effectiveness
Digital is a critical communication channel, but to be valuable, this content must be shared in the right places and in the right way. Organizations should use Digital XM programs to continuously improve their content in order to boost brand perception, deflect support costs, and drive higher conversion.
Omnichannel Feedback
As digital interactions become the primary door through which people engage with an organization, these channels are increasingly crucial for capturing their thoughts and feelings – not only of their digital experiences – but of the organization overall. Digital XM programs should help generate insights about how to improve the company’s products, services, processes, and brand messages.
Product Design
Because digital channels are such an effective venue for uncovering and testing out new offerings, Digital XM programs should be a core driver of organizational innovation. This may be through identifying a potential capability to build out on the website, evaluating the viability of a new app, or even discovering the desire for a new offline product or service.
Digital XM Toolkit
If organizations are going to continuously design and improve their digital experiences, they can’t go about collecting insights from visitors in a random, haphazard way. Instead, they need to carefully architect how they are capturing and analyzing X-data at key moments throughout the entire digital journey.
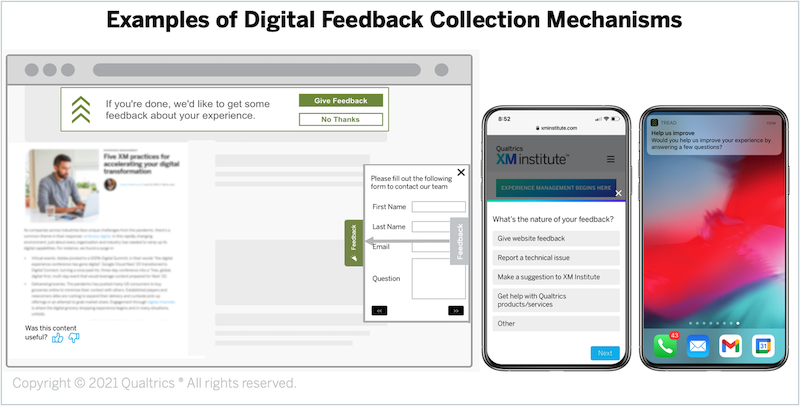
One of the benefits of a digital environment is that organizations have a variety of potential technologies, triggers, formats, and listening posts at their disposal to instrument data collection across these journeys. Here are some of the key tools organizations should consider using to understand and respond to people’s digital experiences:
X-Data Collection Mechanisms
There are a number of different mechanisms organizations can deploy to solicit feedback during a digital experience. Popular approaches include both behavior-based and always-on intercepts, embedded feedback, cross-channel initiation, or – for mobile – in-app notifications. Common digital metrics captured through these mechanisms include satisfaction, ease, and likelihood to return.
Contextual and Embedded Data
Digital channels automatically generate a significant amount of O-data, which organizations can combine with X-data to develop more actionable and predictive insights. Common examples of this type of data include browsing behavior – such as page views, search terms, cart size, new/repeat visitors, and time spent on the site – as well as behaviors “behind the login,” like demographic data, annual spend, and employee organization.
Complimentary O-Data Analytics
Organizations can deepen their understanding of people’s digital experiences by combining insights from complimentary O-data analytic tools – such as session replays or site analytics – with the X-data they’ve collected.
Insight triggers and workflows
Tracking and analyzing people’s experiences alone doesn’t create value. Organizations need to actually act on these insights. They can do this by establishing a comprehensive system of action that integrates digital insights into specific workflows, getting the right information into the hands of the right people at the right time so they can take immediate and meaningful action on it.
Tips for Taking Action
So how should a company go about building its Digital XM capabilities? Here are some tips for taking action:
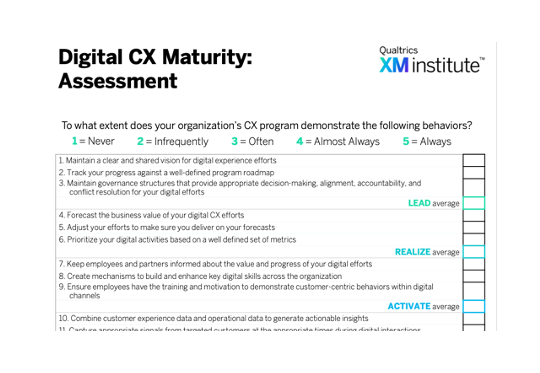
Assess your current maturity level
An organization’s ability to design and deliver easy, emotionally engaging digital interactions doesn’t appear overnight – it will evolve through five stages of maturity. To understand the current state of your digital CX program and develop plans for making progress towards your goals, take the Digital CX Maturity Assessment.
Focus on emotion
While people perceive their experiences with organizations across three dimensions – success, effort, and emotion – the emotion component has the biggest impact on key loyalty behaviors. To create emotionally engaging digital experiences, apply the seven techniques of the Human Conversational Model.
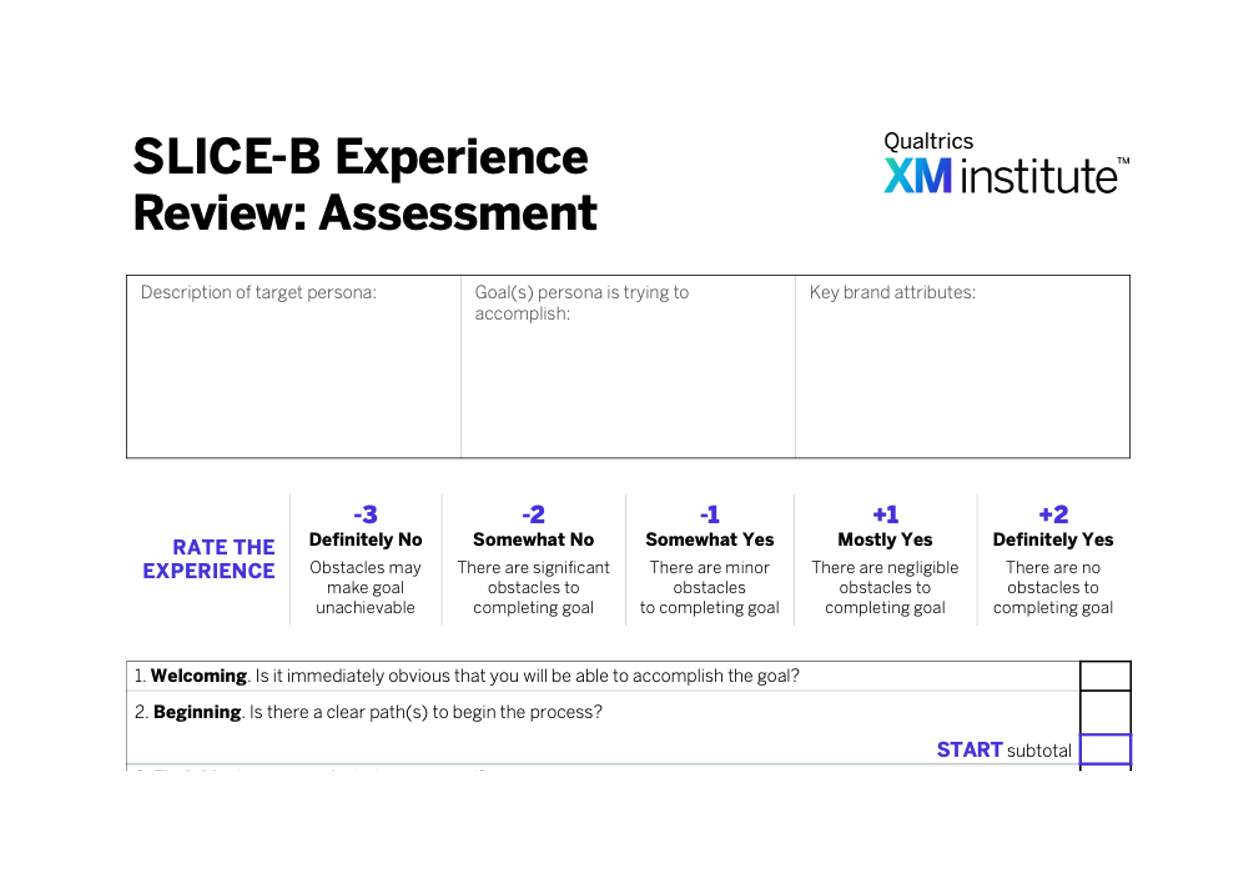
Design around key journeys
To help people reach their goals efficiently, identify and design for the fundamental journeys people take to complete tasks on your digital properties. You can identify these paths through site analytics and survey questions around “visitor intent” or “primary purpose.” To help you find and eliminate issues along a given digital journey, conduct a SLICE-B Experience Review.
Prioritize user experience
Don’t ask visitors for feedback at the cost of the user experience. When requesting feedback in this channel, follow best practices like making sure the design and tone of the feedback request match your brand, keeping the survey short, using compelling language in the solicitation request, and embedding survey targets inside the intercept.
Focus on action, not measurement
Shift your emphasis from measuring digital experiences to acting on the insights you generate through these channels. In addition to diagnostic tools like text analytics and key driver analytics, also deploy tools like predictive intelligence and data integrations and workflows, which will prescribe the best actions a team can take to create business value from digital insights.
Build automated insight workflows
Digital XM enables a unique, often seamless, opportunity to follow up with the people who provide feedback. Establish a closed-loop system by using integrations with applications like Slack, Jira, or Salesforce to share the visitor’s feedback out to the right people across the organization in a format that enables them to quickly respond to and take action on these insights.