Key Findings
As part of Qualtrics XM Institute’s 2024 Global Consumer Study, more than 23,000 consumers around the world shared their preferences for personalization and concerns about personal information privacy. From their responses, we found that:
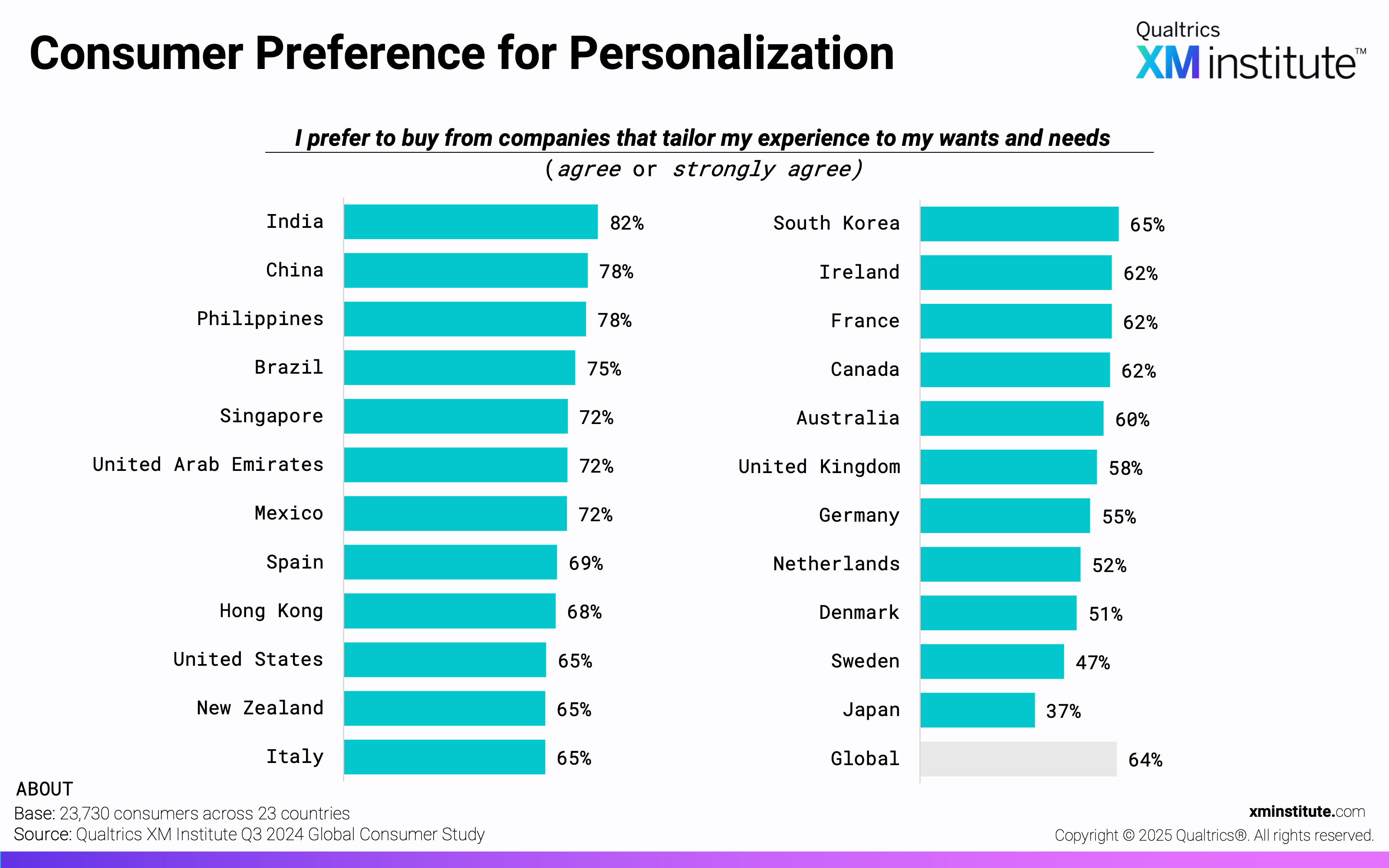
- Consumers want personalization… Globally, 64% of consumers prefer to buy from companies that tailor [their] experience to [their] wants and needs. This preference is strongest in India, where 82% of consumers agree with this statement, and weakest in Japan, where just 37% agree.
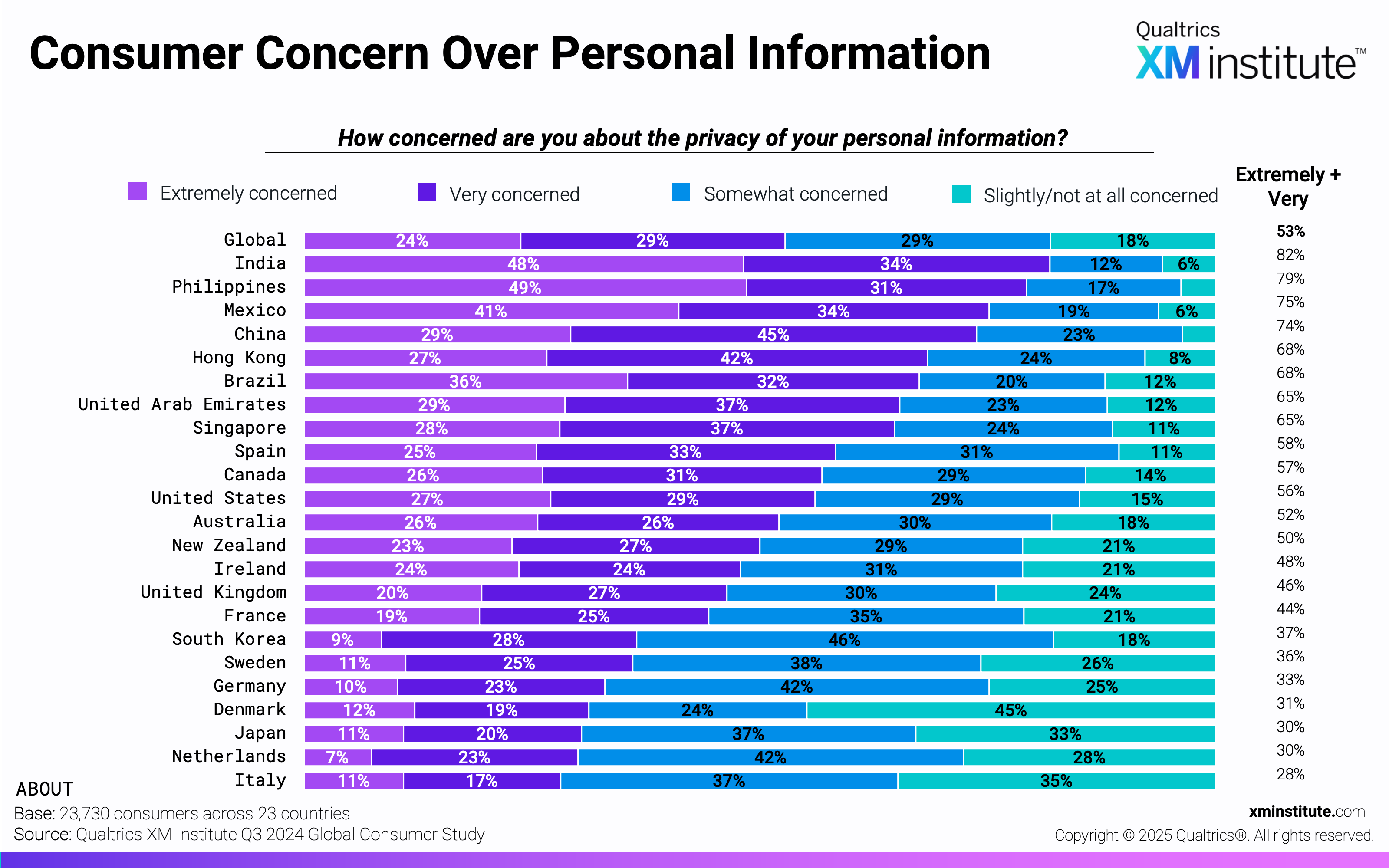
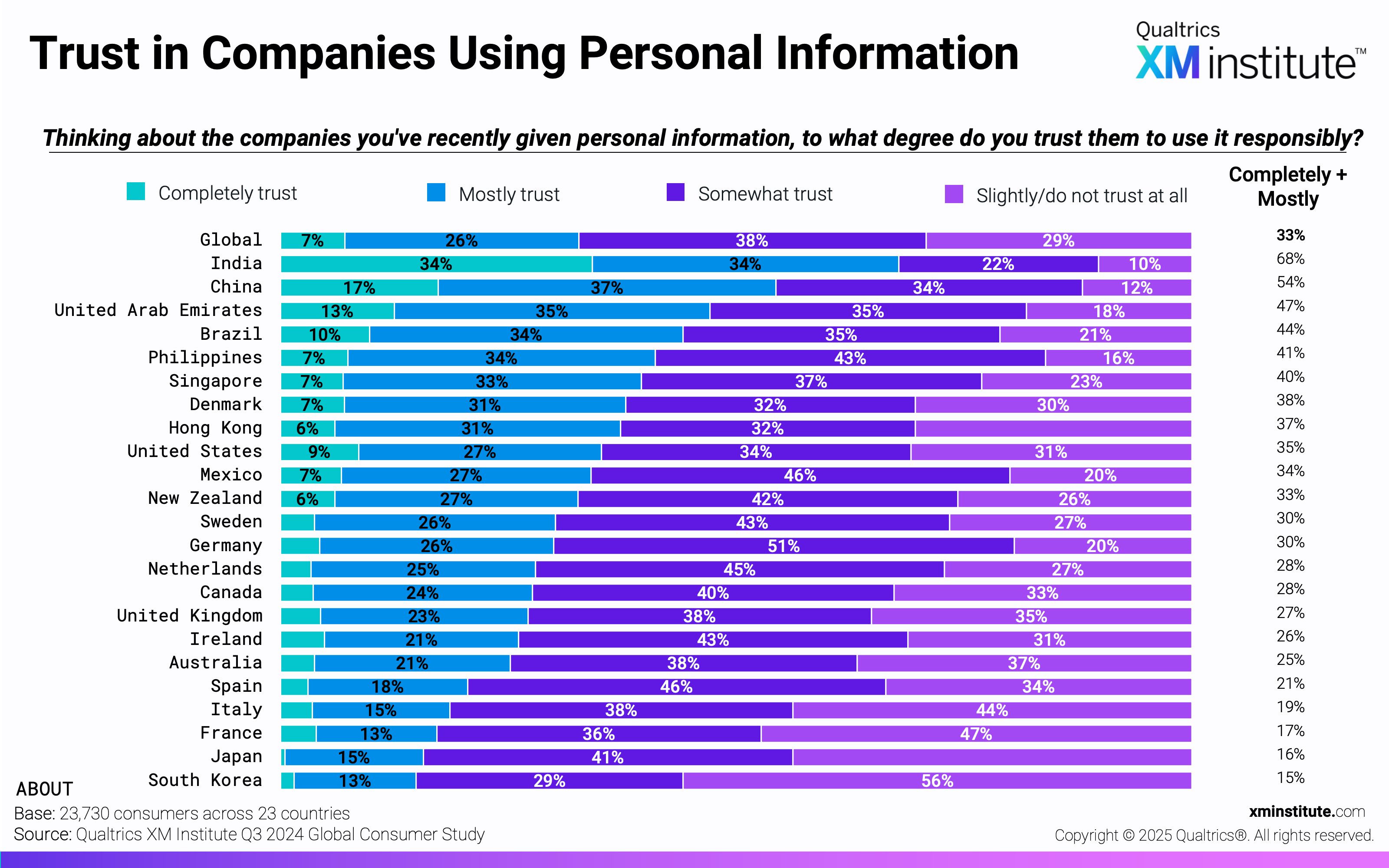
- …Yet are highly concerned about data privacy. Fifty-three percent of consumers are extremely or very concerned about the privacy of their personal information. On average, only 33% trust companies to use their personal information responsibly. EMEA countries are least likely to be concerned about their privacy (42%), yet are also least likely to trust companies to use personal information responsibly (28%).
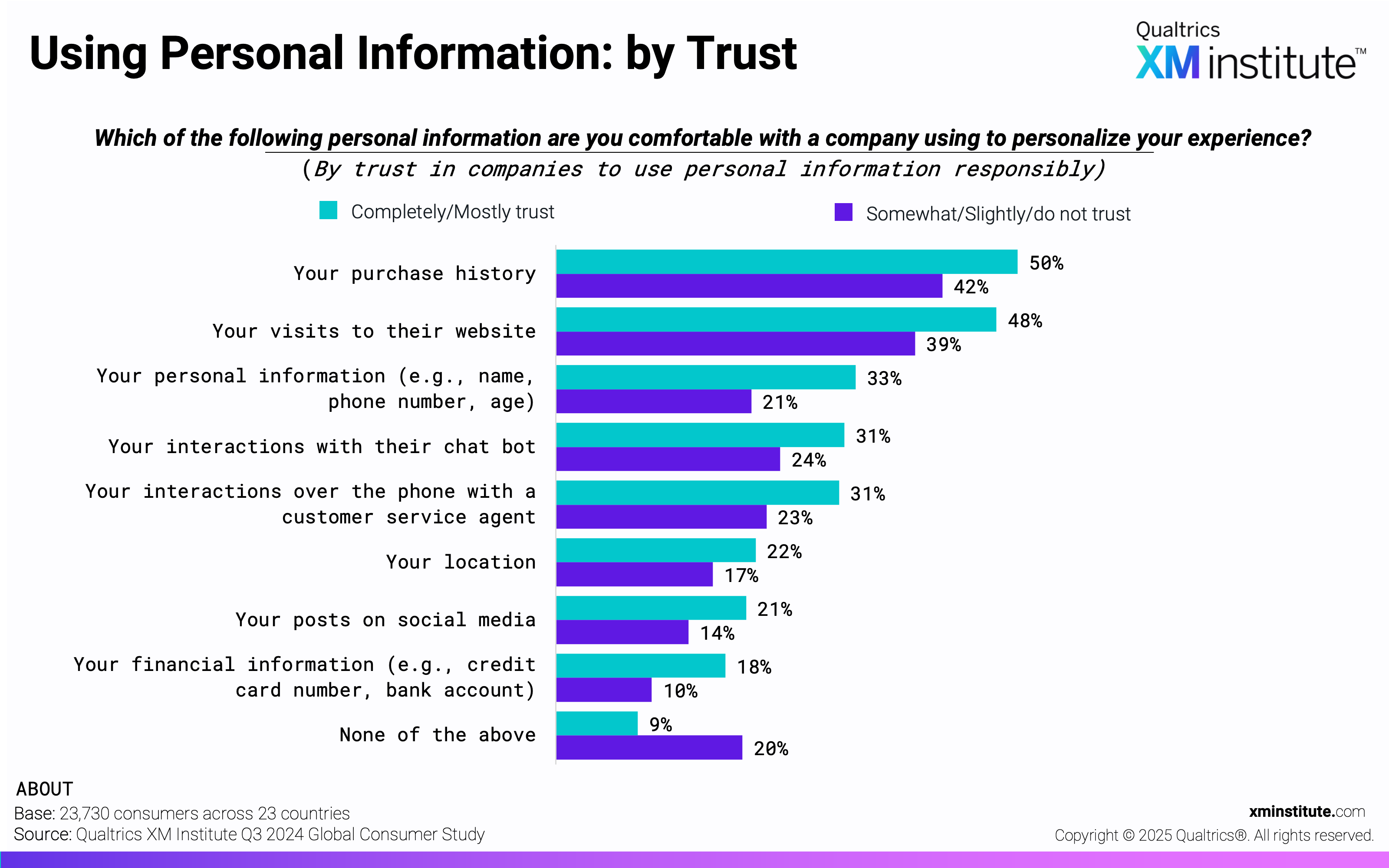
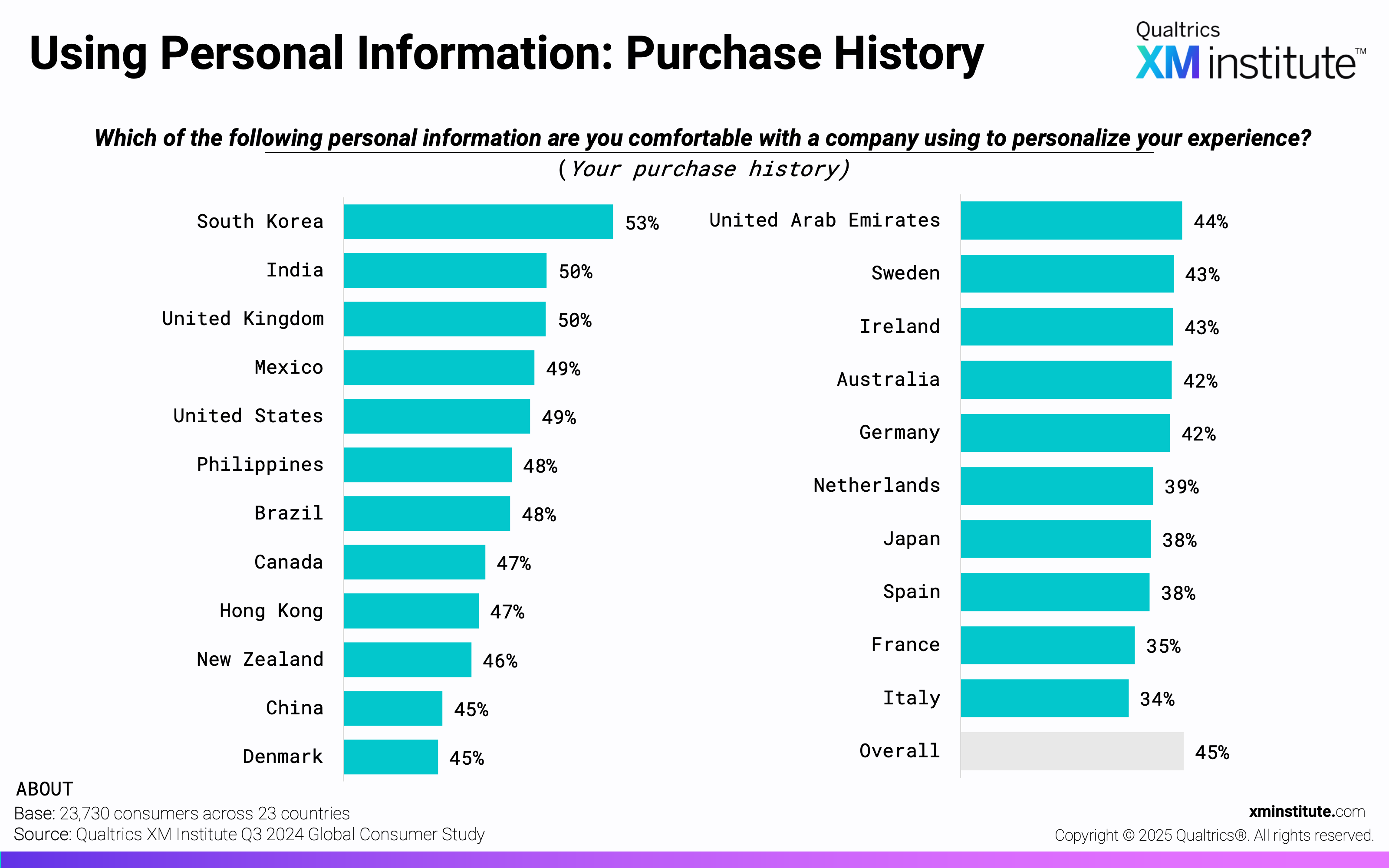
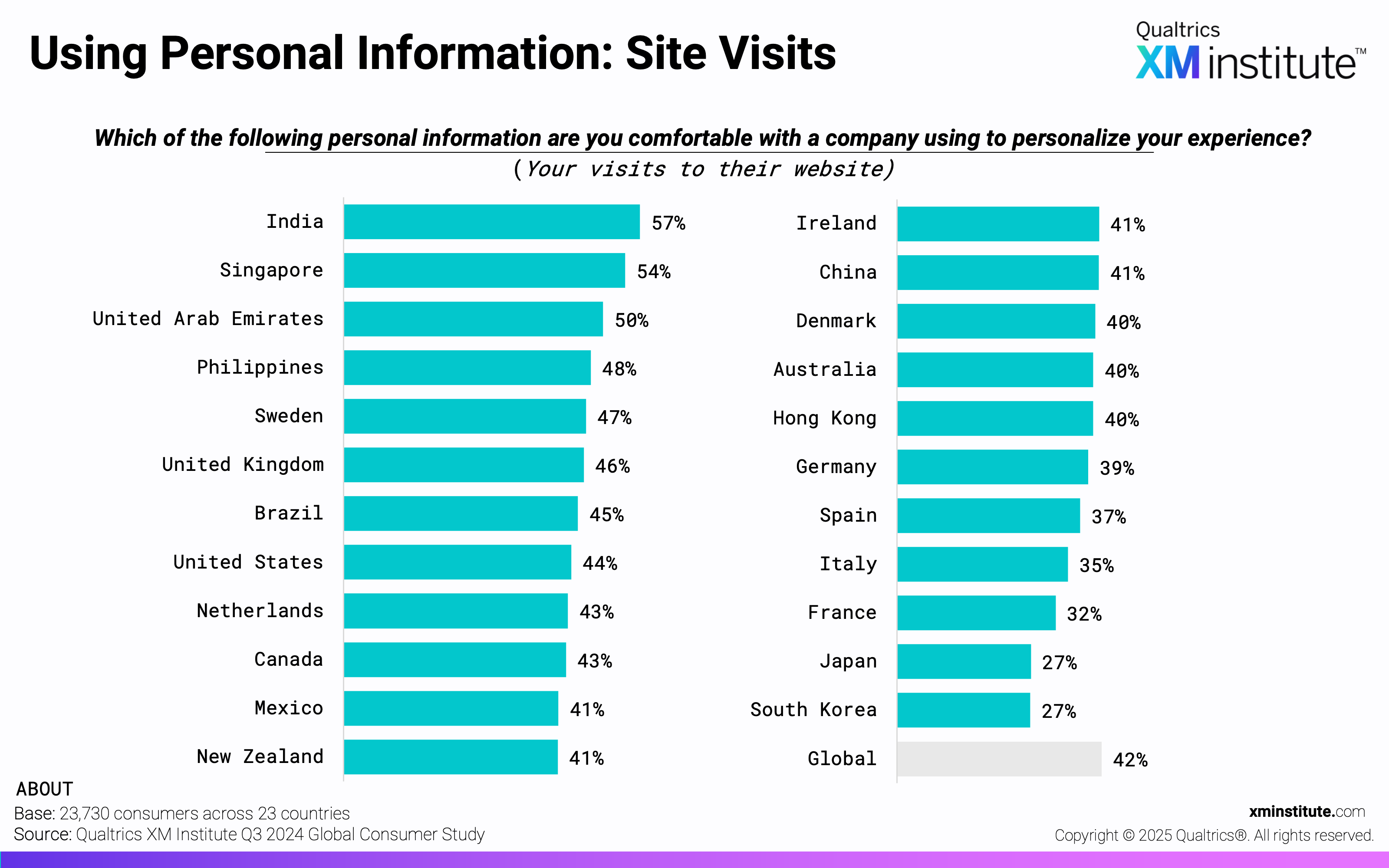
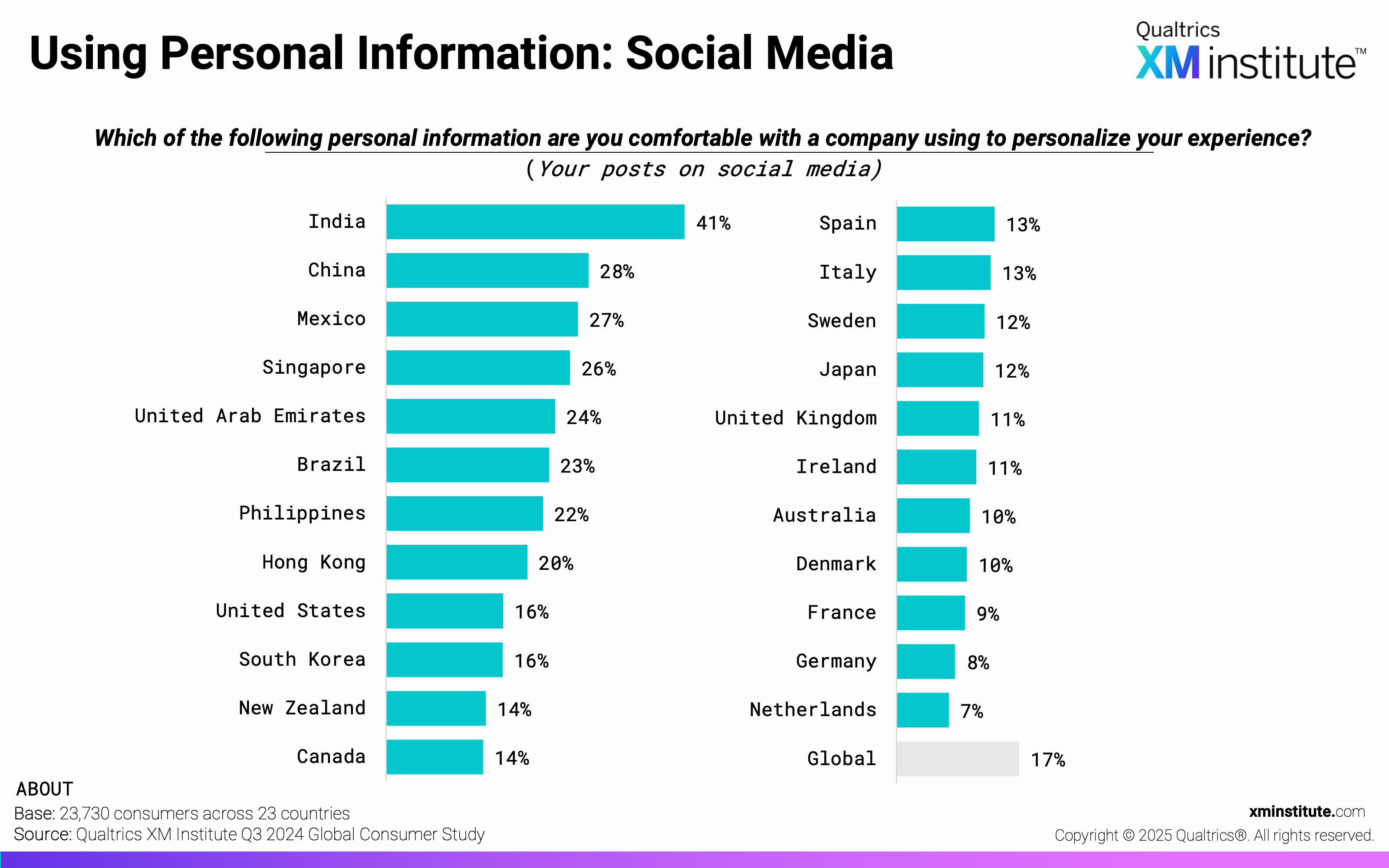
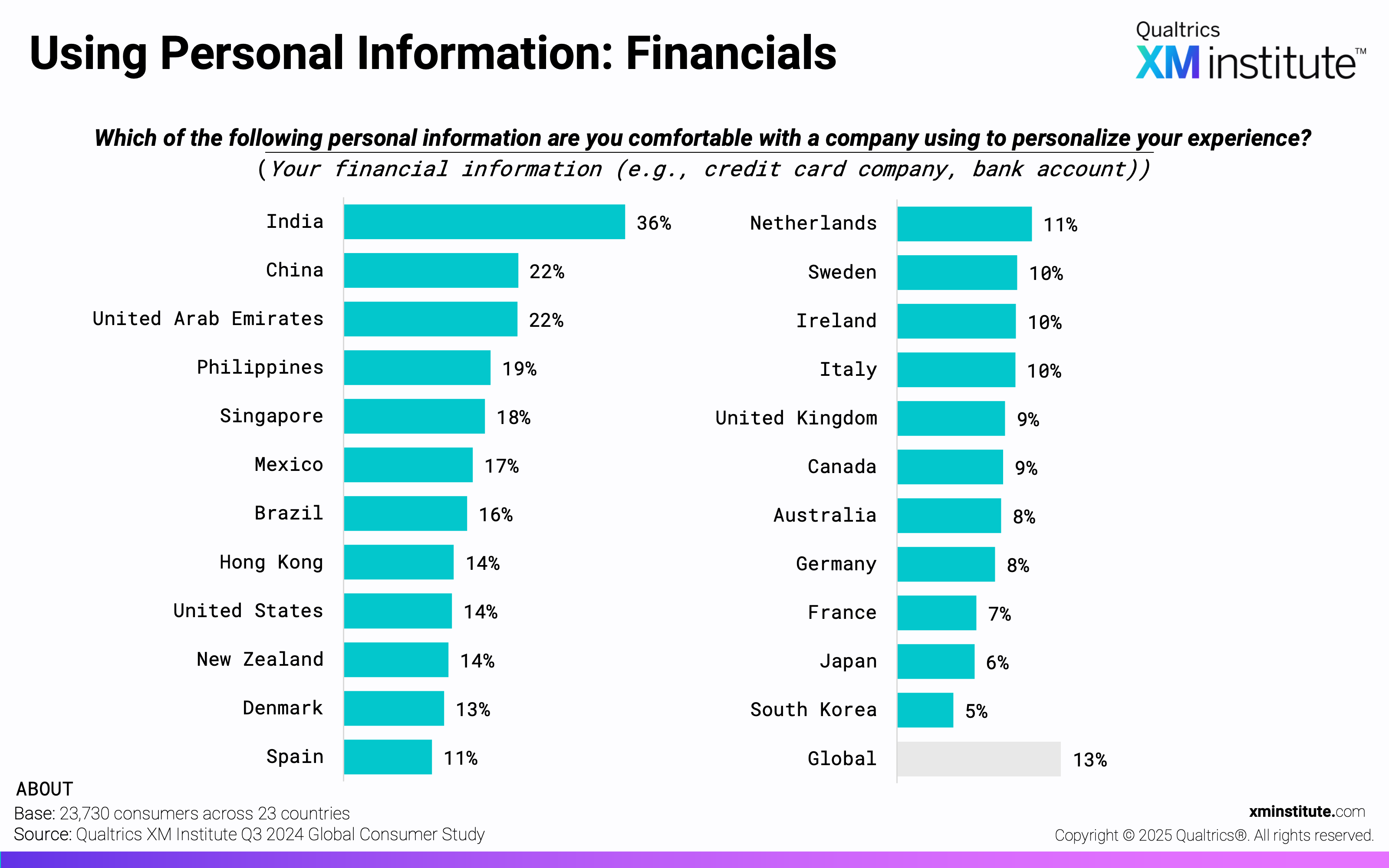
- Purchase history and site visits are top candidates for personalization. Consumers are most comfortable with a company using their purchase history (45%) and website visits (42%) to personalize their experience. They are least comfortable with companies using their financial information (12%) and social media posts (17%).
- Trust in data practices corresponds to comfort with data usage. When consumers trust companies to use their personal information responsibly they are, on average, 8 percentage points more likely to be comfortable with companies using each personal data type to personalize their experience.
- Comfort with data usage for personalization varies by country. French consumers show the lowest comfort level with companies using their information for personalization, averaging 18% across personal data types. Indian consumers profess the most comfort with companies using their data for personalization (43%).
Recommendations
In an increasingly competitive business environment, organizations must meet the needs and desires of consumers. Most consumers want and expect tailored experiences, but harbor concerns over companies using their data in order to do so. To help organizations balance their need for data and the customer need for privacy, we offer three areas of recommendations for customer experience professionals to consider:
- Bridge the trust gap. Organizations must build trust in their data practices for consumers to share information and appreciate the personalized experience the organization provides.
- Collect a variety of XM data. Your customers are the best source of customer information—tap into the Experience Management (XM) data they’re already sharing across a diverse set of touchpoints and channels.
- Use Artificial Intelligence to personalize at scale. Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the business landscape, and these tools can make organizations’ efforts to personalize customer experience more efficient and effective.
Bridge the Trust Gap
Our data shows that consumers who trust companies to use personal information responsibly are more willing to share their data for personalization purposes. Like human relationships, it takes time and effort to build trust. Yes, consumers want personalized experiences and organizations need data to do that. But as a first step, organizations need to prioritize strategies that can develop and maintain trust.
In order to gain consumer trust in your organization’s data practices and increase their willingness to share data, we recommend using these strategies:
- Make your personalization strategies opt-in only. Provide consumers a chance to decide whether they want personalized experiences to ensure those who receive them are more likely to value them. This will reduce the potential that personalization efforts result in moments that harm the brand.
- Be transparent about how you use personal data. Explain to customers how their personal and behavioral data will result in tangible benefits and enhance their experience. This will increase the likelihood consumers engage with your organization and actively share more information.
- Personalize selectively. Focus personalization on moments that matter to ensure your strategies are effective and helpful. During early customer learning phases, personalization may not be beneficial due to limited data availability. In contrast, personalization efforts delivered post-purchase can use numerous transactional and personal data points to offer a more relevant experience.
- Limit the use of second- and third-party data. Using personal information sourced from outside the direct relationship between the brand and the consumer is a risky endeavor. While this data is valuable for building segments, when it comes to personalization efforts, it can create an uncanny experience (e.g., the creepy factor) that leads to consumer disengagement with the brand.
- Protect and respect consumer data. As a basic measure, ensure compliance with all relevant regulatory protocols when handling consumer data.Communicate that your organization takes steps to ensure the safety and responsible management of their data. Make these policies easily accessible and notify consumers of updates to these policies using clear, easy-to-understand language.
Collect a Variety of XM Data
Organizations cannot rely on just one (or even a handful!) of XM data sources to accurately understand a customer. Consumers often share their preferences, interests, and needs through a multitude of channels. Every time a consumer interacts with your organization, they are telling you something meaningful. This data is an invaluable personalization resource and it is your responsibility to collect it and apply it.
Before you can create meaningful and effective personalization strategies, you need to have effective strategies for sourcing this data. Continuously evaluate and adjust your data collection strategies with consideration for changing customer expectations and privacy needs. Examples of some XM data sources you might choose to tap into include:
- Contact Centers. The issues, complaints, questions, and support needs that cause customers to reach out to your organization via calls, chats, and chat bot interactions are a window into what your customer cares about. In addition to the topics they call in about, the sentiment and effort required by your agents during these conversations can inform how to best communicate with your consumers.
- Communities. Brands can build communities or connect with existing communities (e.g., Reddit) to learn about their consumers’ needs. Like contact centers, the data here is rich with context about individual interests, needs, and engagement with the brand. As a bonus, these channels also offer a direct path to engage with your consumers and deepen relationships.
- Digital Channels. Collect unsolicited data like website or app analytics that can tell you what consumers are interested in without asking; the consumer is already doing the heavy lifting by engaging with a channel you own.
- Quizzes. These can be a tool to help consumers identify relevant products or services and also act as a resource for the brand when building robust customer profiles.
- Newsletter Sign Ups. All touchpoints where a customer willfully engage with you are moments for you to gather useful personal information, including newsletters sign-ups, which offer a chance to understand the content preferences and priorities of your customers.
- Loyalty Programs. When your consumers join or interact with a loyalty program, take the opportunity to decipher what they find meaningful about the program. You can use this information later to deliver and personalize future offers or recommendations.
- Surveys. Every survey is an opportunity to get feedback; just as importantly, it’s an opportunity to learn. Weave in questions relevant to the experience that can inform future experience delivery as a light-touch method of collecting useful personal data.
Use Artificial Intelligence to Personalize at Scale
Historically, personalization has been a labor-intensive effort. But with Artificial Intelligence (AI), organizations are increasingly able to streamline and scale the delivery of personalized experiences to individuals’ preferences and needs. To reduce the effort required to activate available customer information and personalize experiences, companies should explore the use of AI to:
- Automate segmentation. Use AI-powered tools to more easily identify trends, insights, and patterns from XM data and group customers into segments based on sets of shared characteristics including preferences, behavior, and sentiment. AI tools can also enable the continuous refinement and evolution of these segments as new data becomes available.
- Tailor communications. Many organizations have already tapped into the capabilities that Generative AI offers to enhance and accelerate their content production. AI-powered tools can also enable companies to adapt all aspects of customer communications to fit a particular segment’s expectations and preferences. Organizations that tap into these tools will be able to personalize the communication style and tone of their content to different audiences and identify the optimal timing and channels based on customer behaviors. For example, you may segment customers who tend to open emails at night, or those who are more likely to click on push notifications from an app – AI tools can help you select and send the right messaging to the right customer segment at the right time.
- Customize Interactions. With enough context, organizations will be able to automatically adjust interfaces and content to individual customers. Organizations that use AI-powered tools will be able to develop digital interfaces and imagery that can adapt to a customer’s preferences and personalize the customer journey flows based on customer context and behavior.
Figures
Here are the figures in this Data Snapshot:
- Consumer Preference for Personalization (see Figure 1)
- Consumer Concern Over Personal Information (see Figure 2)
- Trust in Companies Using Personal Information (see Figure 3)
- Using Personal Information: Global (see Figure 4)
- Using Personal Information: by Trust (see Figure 5)
- Using Personal Information: Purchase History (see Figure 6)
- Using Personal Information: Site Visits (see Figure 7)
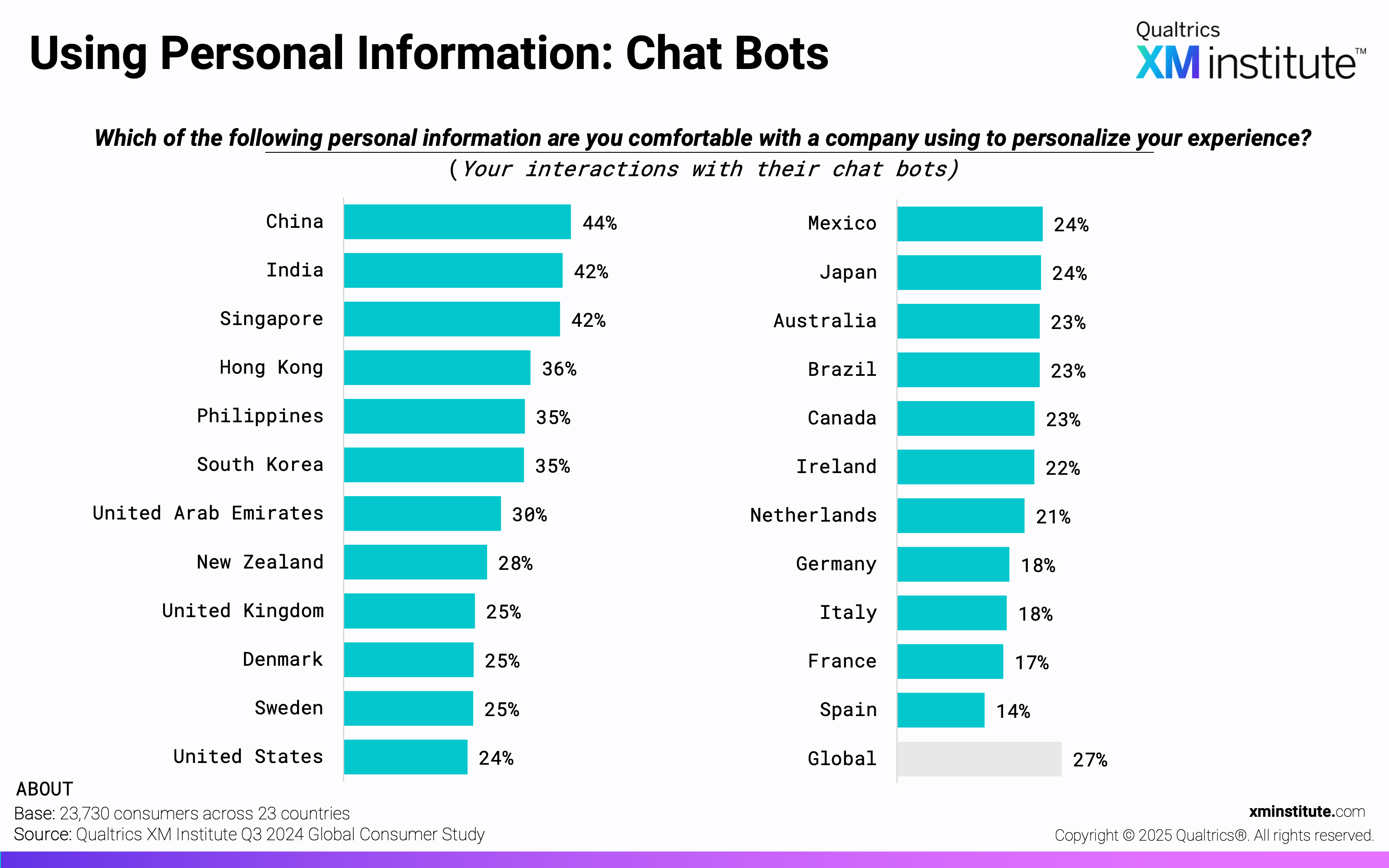
- Using Personal Information: Chat Bots (see Figure 8)
- Using Personal Information: Agent Interactions (see Figure 9)
- Using Personal Information: Identification (see Figure 10)
- Using Personal Information: Location (see Figure 11)
- Using Personal Information: Social Media (see Figure 12)
- Using Personal Information: Financials (see Figure 13)
- Methodology (see Figure 14)